Redshift
- Amazon Redshift is a fully-managed petabyte-scale cloud-based data warehouse product designed for large scale data set storage and analysis.
- Can be used for online analytical processing
- Amazon Redshift mostly only supports Single-AZ deployments:
- some clusters are compatible with Multi-AZ
- Redshift is based on PostgreSQL
- It’s not used for online transaction processing
- Rather it is OLAP
- Online analytical processing
- analytics and data warehousing
- 10x better performance than other data warehouses
- Scale to PBs of data
- Columnar storage of data (rather than row-based)
- Parallel query engine
- Has SQL interface for performing the queries
- Any business intelligence tools integrate with it, such as:
Redshift vs Athena
- in redshift, you must load the data
- Redshift has indexes (Athena doesn’t). Thus,
- Redshift is going to have much faster queries
- Redshift can do much faster joins
- Faster integration
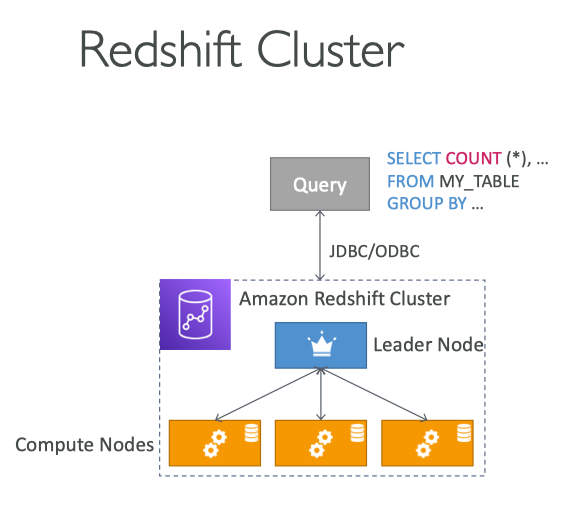
Redshift Cluster
- Leader node
- query planning
- results aggregation
- Compute node
- performing the queries
- send results to leader
- Node size is provisioned in advance
- Use Reserved Instances for cost savings
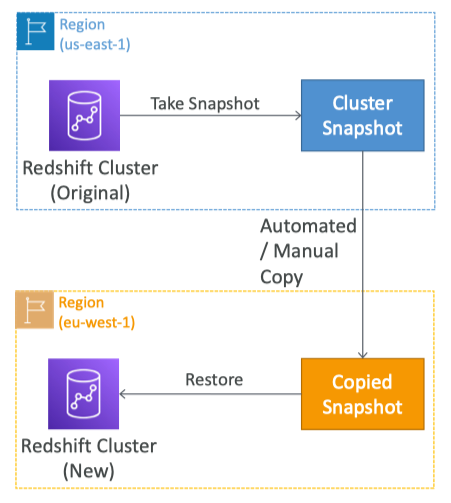
Snapshots and Disaster Recovery
- Redshift has multi-AZ mode for some clusters
- Snapshots
- point-in-time backups of a cluster
- Incremental
- Can be restored into a new cluster
- Automated
- every 8 hours
- every 5 GB
- on a schedule
- set retention
- Manual
- snapshot is retained until you delete it
- You can configure Amazon Redshift to automatically copy snapshots (automated or manual) of a cluster to another AWS Region
- Provides a DR config ability
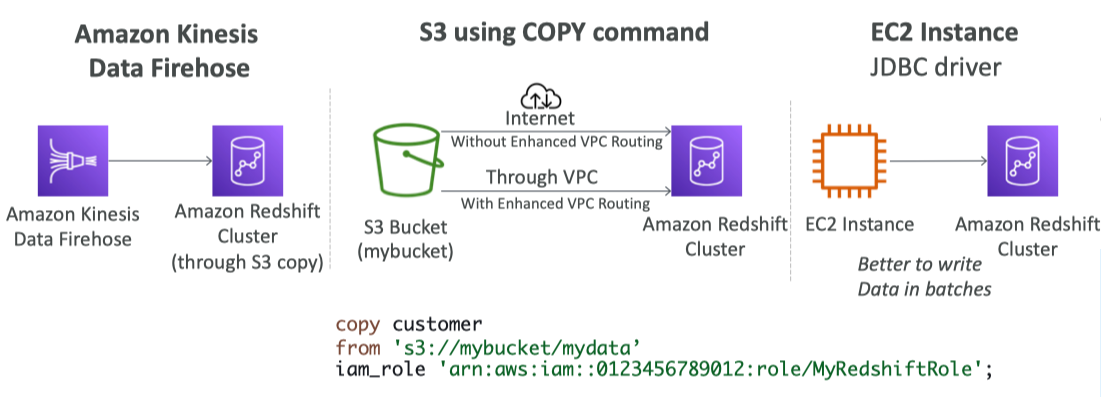
Loading Data into Redshift
- Large inserts are much better
- Large batches of data = efficient
- one row at a time = wildly inefficient
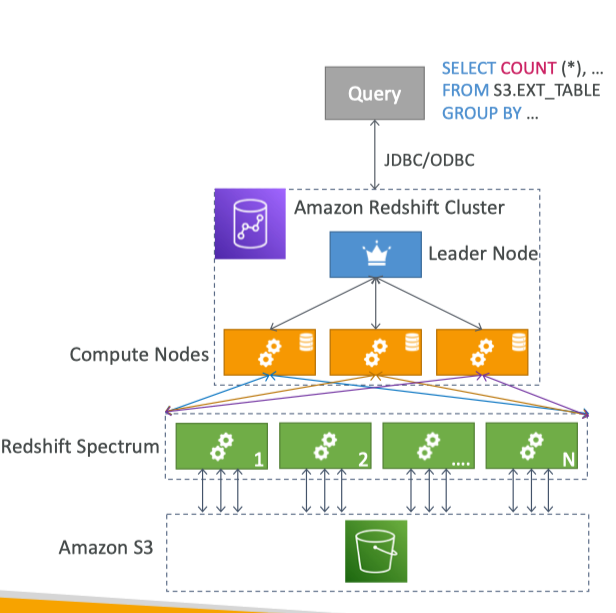
Redshift Spectrum
- Query data that is already in S3 without loading it
- Must have a Redshift cluster available to start the query
- Query is then submitted to thousands of Redshift Spectrum nodes
Pricing
- Pay-as-you-go based on instances provisioned



