Overview
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a scalable object storage service provided by AWS that allows you to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere on the web. It is designed to deliver 99.999999999% durability and provides a simple web services interface to store and retrieve any amount of data at any time.
- S3 is a key/value store for objects
- great for bigger objects, not so much for many small objects
- Serverless
- scaled infinitely, max object size is 5TB
- versioning capability
- Tiers
- Standard
- Infrequent access
- Intelligent
- Feaures
- versioning
- encryption
- replication
- MFA-Delete
- Access Logs
- Security
- Encryption
- SSE-S3
- SSe-KMS
- can bring own KMS key
- SSE-C
- client-side encryption
- TLS in transit encryption
- default encryption
- Batch Operations
- on objects using S3 Batch
- listing files using S3 Inventory
- Performance:
- Multi-part upload
- S3 Transfer Acceleration
- S3 Select
- Automation
- S3 Event Notifications
- Use cases
- static files
- key value store for big files
- website hosting
- redirect ability contained therein
S3 Storage Classes
S3 Standard
S3 Standard-IA
S3 Intelligent Tiering
S3 Express One-Zone
S3 Glacier Instant Retrieval
S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval
S3 Glacier Deep Archive
S3 One Zone - IA
S3 Cross Region Replication
Pricing
Data Transfer Pricing (section incomplete)
Pricing for S3 ingress from internet
- always free
Pricing for S3 egress to internet
- Free for the first 100 GB out per month. After that, t follows tiered pricing, with discounts being rewarded by tiers:
- First 10 TB/Month
- $0.09 per GB
- Next 40 TB/Month
- $0.085 per GB
- Next 100 TB/Month
- $0.07 per GB
- Greater than 150 TB/Month
- $0.05 per GB
- First 10 TB/Month
Pricing for S3TA ingress from net
-
Accelerated by AWS Edge Locations in the United States, Europe, and Japan
- $0.04 per GB
-
Accelerated by all other AWS Edge Locations
- $0.08 per GB
Pricing for S3TA egress to net
-
Accelerated by any AWS Edge Location
- $0.04 per GB
Data Transfer between Amazon S3 and another AWS region:
-
Accelerated by any AWS Edge Location
- $0.04
For Data Transfers exceeding 500 TB/Month
- Contact AWS
Per class pricing
(uses us-east-1 guidelines)
S3 Standard Pricing
- First 50 TB / Month
- $0.023 per GB
- Next 450 TB / Month
- $0.022 per GB
- Over 500 TB / Month
- $0.021 per GB
S3 Standard IA Pricing
- All Storage / Month
- $0.0125 per GB
S3-Intelligent tiering Pricing
Monitoring and Automation
- All Storage / Month (Objects > 128 KB)
- $0.0025 per 1,000 objects
Frequent Access Tier
Shares the same pricing with S3 Standard
- First 50 TB / Month
- $0.023 per GB
- Next 450 TB / Month
- $0.022 per GB
- Over 500 TB / Month
- $0.021 per GB
Infrequent Access Tier
Half the cost of FA Tier!!!
- All Storage / Month
- $0.0125 per GB
Archive Instant Access Tier
Over 80% cheaper than FA tier!!!
- All Storage / Month
- $0.004 per GB
Archive Access Tier
- All Storage / Month
- $0.0036 per GB
Deep Archive Access Tier
- All Storage / Month
- $0.00099 per GB
S3 Express One Zone Pricing
Lifecycle transitions
Amazon S3 supports a waterfall model for transitioning between storage classes, as shown in the diagram below:
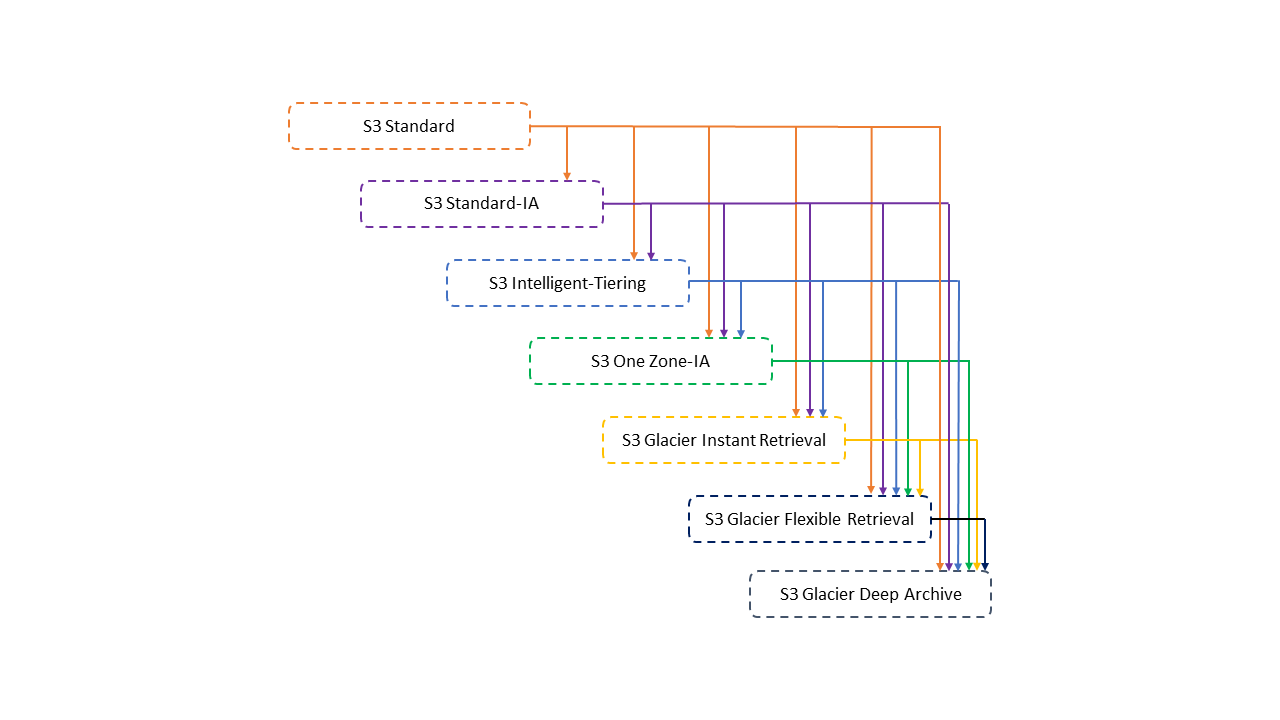
Supported lifecycle transitions
- S3 Standard to ANY other storage class
- Any storage class to the S3 Glacier or S3 Glacier Deep Archive storage classes
- S3 Standard-IA storage class to the S3 Intelligent-Tiering or S3 One Zone-IA storage classes
- The S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class to the S3 One Zone-IA storage class
- The S3 Glacier storage class to the S3 Glacier Deep Archive storage class.
Unsupported lifecycle transitions
- ANY storage class to the Amazon S3 Standard storage class.
- Any storage class to the Reduced Redundancy storage class.
- Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class to the Amazon S3 Standard-IA storage class.
- The Amazon S3 One Zone-IA storage class to the Amazon S3 Standard-IA or Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage classes.
Minimum storage duration for transitioning
- 30 days before transition from S3 Standard to S3 Standard-IA
- 30 days before transition from S3 Standard-IA One-Zone IA
S3 Req Types
PUT
COPY
POST
LIST
GET
SELECT
DELETE
CANCEL
Livecycle Transition
Data Retrievals
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
- Origin = scheme (protocol) + host (domain) + port
- Browser-based mechanism to allow reqs to other origins while visiting main origin
- Reqs wont be fulfilled unless the other origin allows for the requests, using CORS Headers
- example: Access-Control-Allow-Origin
How it applies to S3
- If a client makes a cross-origin request on our bucket, correct CORS headers need to be enabled
Requester Pays
- Bucket Owner still pays storage costs BUT requester pays for cost of data request and data download from the bucket
- The requester cannot be anonymous and must be aws-authenticated
Performance
Baseline performance
- s3 auto-scales to high req rates
- latency: 100-200 ms
- 3500 reqs/sec/prefix for request types:
- PUT
- COPY
- POST
- DELETE
- 5500 reqs/sec/prefix for request types:
- There are no limits to the number of prefixes in a bucket
- this means you can spread demand across multiple prefixes to achieve super-high req rates, even if they are being made to the same parent bucket
Optimizing Performance
Multi-Part upload
- Parallelizes uploads
- recommend for files larger than 100mb
- must use for files larger than 5GB
S3 Transfer Acceleration
- Tranfer to edge location first then forwards data to s3 bucket
- combitible with multi-part
S3 Byte-Range Fetches
- Parallizes downloads by requesting specific byte ranges
- Better resilience in case of failures
- also use to download specific parts of a file
S3 Select & Glacier Select
- retrieve less data using SQL by performing server-side filtering
- Filter by rows and columns (simple sql statements)
- Less network transfer, less cpu cost client-side
S3 Batch Operations
- bulk operations on existing s3 objects with single request
- mod metadata and properties
- copy between s3 buckets
- encrypt un-encrypted objects
- Modify ACL’s, tags
- Restore from s3 glacier
- invoke lambda function to perform custom action on each object
- Job consists of
- List of objects
- Action to perform
- optional parameters
- S3 batch operations does the following
- manages retries
- tracks progress
- sends completion notifications
- generates reports
- Use s3 inventory to get object list and use s3 Select to filter your objects
S3 Storage Lens
- Understand,
Object Encryption
- Use one of 4 available methods
Server side methods (3)
Server-Side Encryption with Amazon S3-Managed Keys (SSE-S3) - Enabled by Default
- Encrypts S3 objects using keys handled, managed, and owned by AWS
- Encryption type: AES-256
- Must set header “x-amz-server-side-encryption”: “AES256”
- Enabled by default for new buckets & new objects
Server-Side Encryption with KMS Keys stored in AWS KMS (SSE-KMS)
- Leverage AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) to manage- encryption keys
- Advantages
- user control
- audit key usage in CloudTrail
- Must set header “x-amz-server-side-encryption”: “aws:kms”
Limitations
Server-Side Encryption with Customer-Provided Keys (SSE-C)
- When you want to manage your own encryption keys
- s3 does NOT store the key you provide
- Must use HTTPS
- Must pass the key, provided in HTTP headers, for every request being made
Client Side
- Use client libraries, such as Amazon s3 client encryption library
- Client must encrypt/decrypt data themselves when sending/receiving s3 data
Encryption in transit (SSL/TLS)
- S3 exposes two endpoints
- HTTP endpoint
- non encrypted
- HTTPS
- encryption in flight
- HTTP endpoint
Forcing encryption in transit (aws:SecureTransport)
Bucket policies
- Always evaluated before you default encryption settings
MFA Delete
- Required to:
- PErmanently delete an object version
- Suspend versioning
- Not required to:
- Enable versioning
- List deleted versions
- versioning must be enabled to use MFA delete
- Only root can enable/disable
S3 Access Logs
- For audit purpose, you may want to log all access to buckets
- Any req made to s3, from any account, authorized or denied, will be logged into another s3 bucket
- The target butcket must be in the same region
- Log format can be examined at: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/LogFormat.html
- Be wary of creating a logging loop by configuring the targetbucket to be the same as the monitored one.
Pre-Signed URLs
- Generate pre-signed URLs using:
- S3 Console
- AWS CLI
- AWS SDK
- Expiration
- s3 console
- 1-720 mins (720 mins = 12 hours)
- AWS CLI -
- use -expires-in parameter in seconds
- default = 3600 secs
- max = 604800 secs ~168 hours
- s3 console
- Users given the presigned URL inherit permisions of the user that generated it for GET/PUT reqs
- Examples
- Allow only logged-in users to download a premium video from your S3 bucket
- Allow an ever-changing list of users to download files by generating URLs dynamically
- Allow temporarily a user to upload a file to a precise location in your S3 bucket
S3 Lock
Glacier Vault Lock
- Adopt a WORM (write once read many) model
- Create a vault lock policy
- Lock the policy for future edits
- Helpful for compliance and data retention
Object Lock
- Versioning needs to be enabled
- Adopt a WORM model
- block an object version deletion for a specified amount of time
Retention Modes
Compliance retention mode
- object versions cant be overwritten or deleted by any user, including root
- retention mode cannot be changed and retention periods cant be shortened
Governance retention mode
- most users cant overwrite or delete an object version or alter its lock settings
- some uses have special perms to change the retention or delete the object
Legal Hold
- protect the object indefinitely, independent from retention period
- can be freely placed and removed using the s3:PutObjectLegalHold IAM permission
Access Points
Object Lambda
- Left off - Video 14015